How to Use Zerto with Google Cloud VMware Engine for Disaster Recovery
With the release of Zerto 8.0, we announced our partnership with Google Cloud for disaster recovery and data protection. Google Cloud VMware Engine enables you to run VMware native workloads in Google Cloud. Zerto customers have a new option for their recovery sites with Google Cloud VMware Engine. Since VMware workloads are running on VMware Cloud Foundation, Zerto customers can use Zerto features in Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Google Cloud VMware Engine recently became generally available and we were delighted to be part of the Google Cloud VMware Engine’s ecosystem as the mission-critical disaster recovery partner. Through our partnership, we recently completed testing disaster recovery and data protection from our lab to Google Cloud VMware.
Zerto and Google Cloud VMware Engine
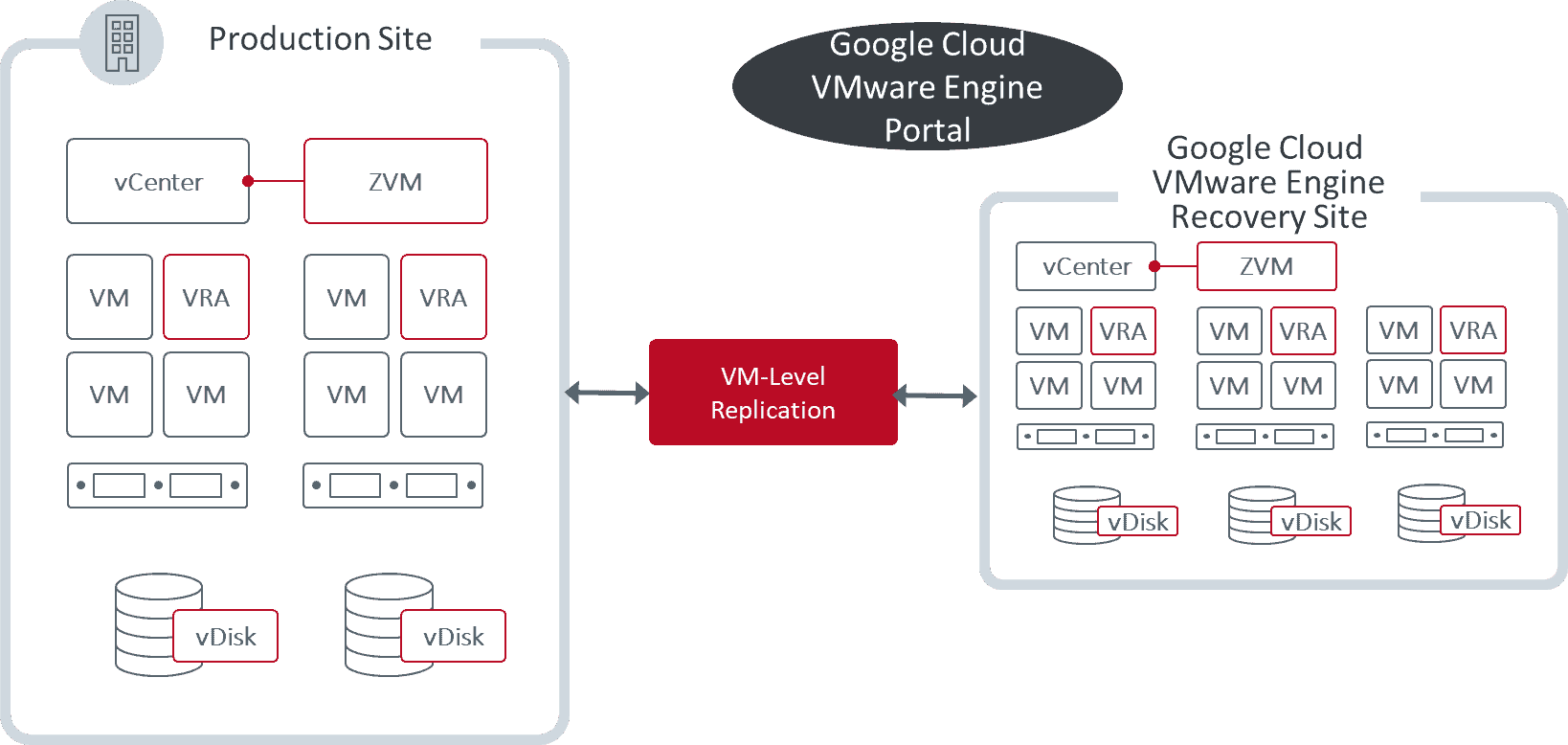
Just like our early adopter customer, QAD, our test team easily set up the connection to our private cloud in Google Cloud VMware Engine. We then deployed the Zerto components into the private cloud on a 3-node cluster. The deployment looked like the below representation.
In our deployment, our lab was simulating a production site on the left and we connected to the Google Cloud VMware Engine recovery site.
Replication from Zerto to Google Cloud VMware Engine
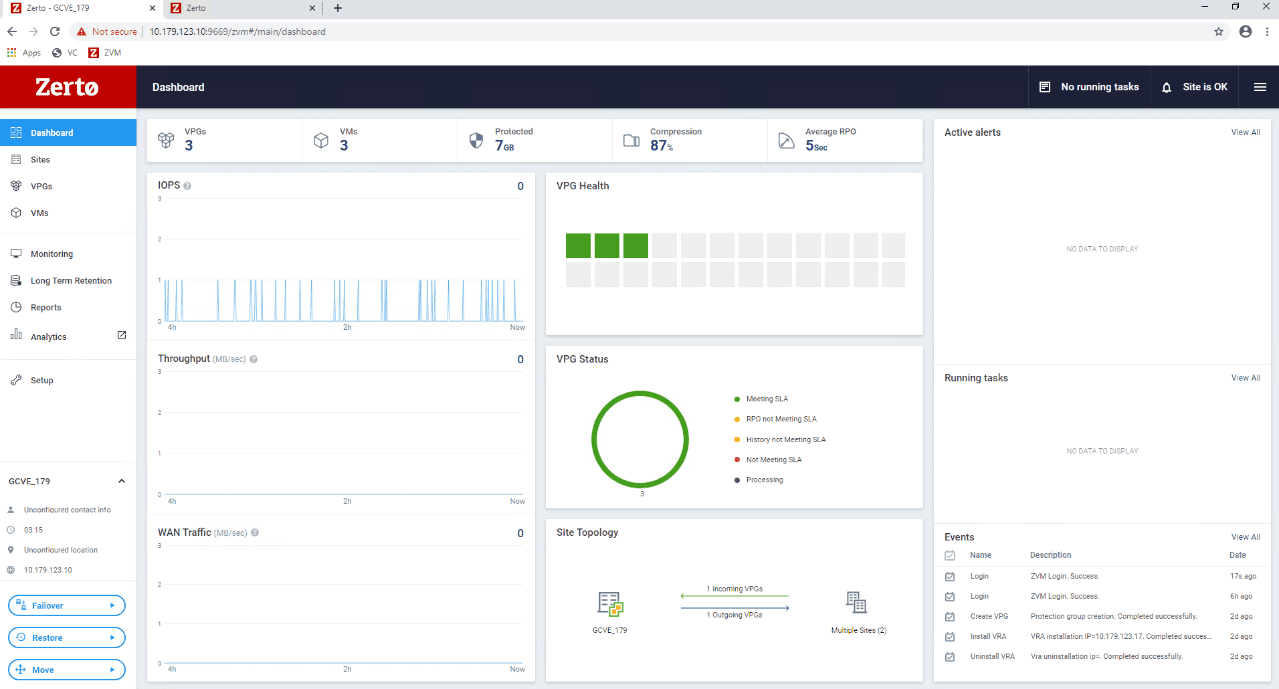
After the initial sync between our lab and the recovery site in Google Cloud VMware Engine, we had the below display on the Zerto dashboard. The Zerto dashboard shows us protecting 3 VMs with 7 GB and an average RPO of 5 seconds.
Disaster Recovery from Zerto to Google Cloud VMware Engine
Next, we simulated a DR event by failing over from our lab to the recovery site. We checked that our failed over VMs were operating nicely in Google Cloud VMware Engine. We then simulated recovery from the DR event by recovering the VMs back to our lab. We saw the VMs recover back to normal operation in our lab.
Workload Migration from Zerto to Google Cloud VMware Engine
After validating a DR event, we next checked that Zerto can move workloads over to Google Cloud VMware Engine and verified the workloads ran fine in their migrated VMs.
Disaster Recovery Test from Zerto to Google Cloud VMware Engine
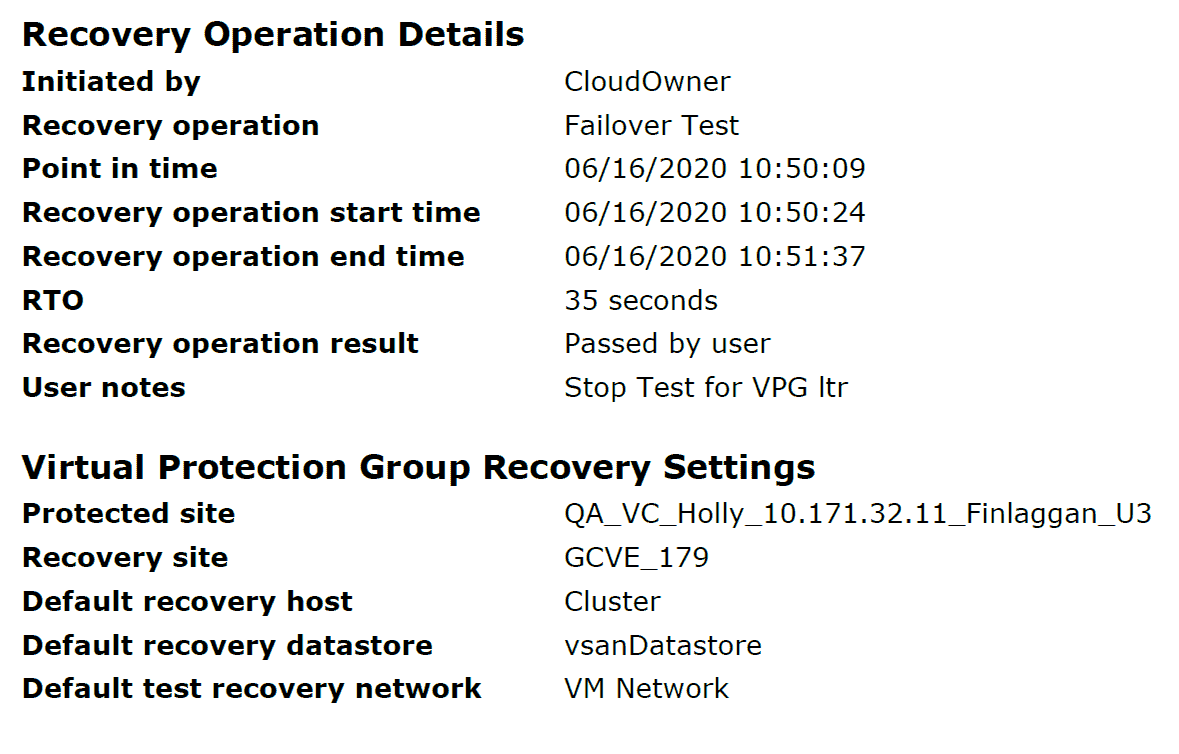
Now that we proved to ourselves that we can handle a DR event as well as workload migrations, we wanted to run a failover test to verify that our protected VMs operate as expected in a DR event. We ran our typical failover test which creates test VMs in the Google Cloud VMware Engine recovery site with one of the recent RPO checkpoints. We saw the test VM power on and start using a scratch volume in the Google Cloud VMware Engine recovery site. The test report is below:
The above failover test report shows we had an RTO of 35 seconds. The RTO consisted of creating the VM, creating the scratch volume, attaching the scratch volume and powering on the VM.
Adding Resources to Google Cloud VMware Engine
We then continued testing our normal suite of VMware platform tests in this environment. Our final test was using the Google Cloud VMware Engine portal to add a 4th node to our private cloud. The new node showed up in only a few minutes after we put it in the Google Cloud VMware Engine portal. We installed a VRA and quickly had replication going to all 4 nodes in our private cloud.
Zerto and Google Cloud VMware Engine
With the completion of our testing, we’ve updated our Interoperability matrix to show we are in controlled release with Google Cloud VMware Engine. We also published our Best Practices for deploying with VMware-as-a-Service to provide information to our customers about what we learned in testing with Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Conclusion
We plan to continue in controlled release with a few Zerto customers to be sure this configuration is documented well and scales with our customers’ needs. If you are interested in joining the controlled release of Zerto with Google Cloud VMware Engine, then please sign up for the program here.
 Amy Mitchell
Amy Mitchell